When (and How) Should You Use a DC EV Charger? The Difference Between AC and DC Current
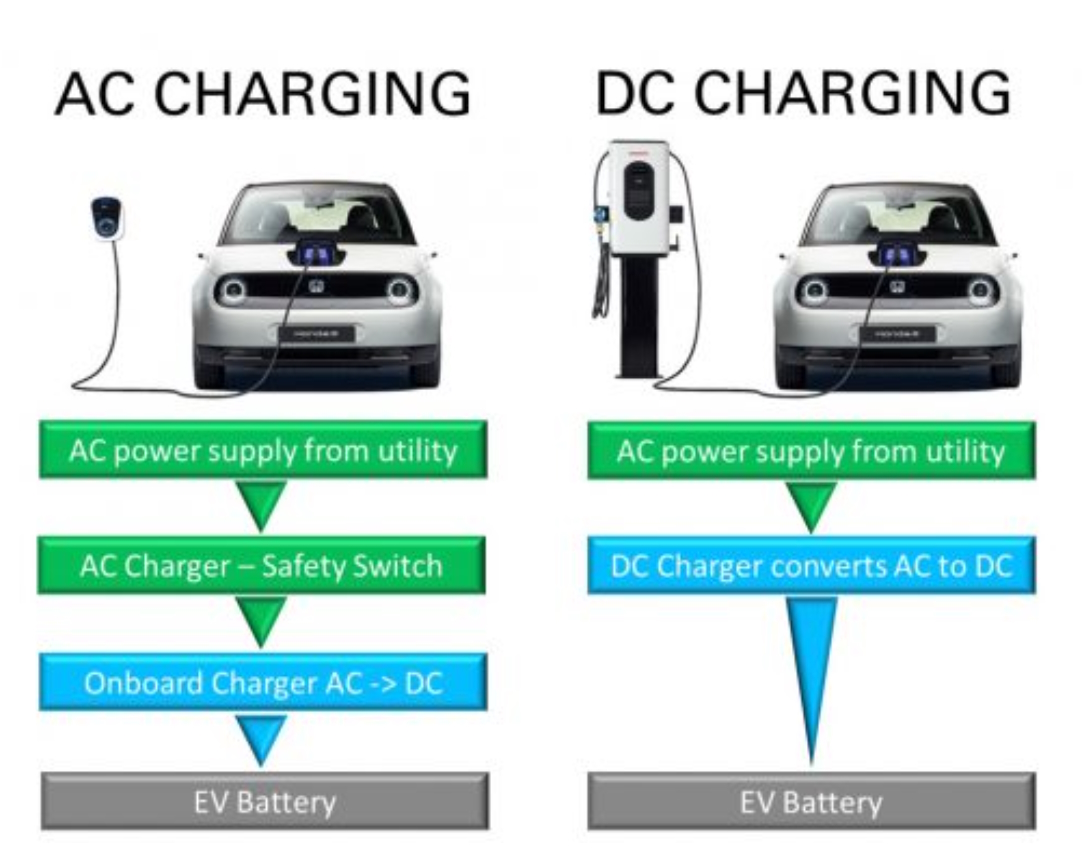
- Electrical current comes in two forms: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). AC is the type of electricity that flows through power grids and into homes and businesses, including to power EV chargers. DC is the type stored in batteries. AC can be thought of as “low and slow” charging, while DC is very fast and powerful.
- The key difference between AC and DC for EV charging is the power level. AC EV chargers operate at lower power levels, usually 7-22kW, which enables slower charging. DC EV chargers can provide much faster charging, with power levels over 50kW or up to 100kW and beyond. This makes DC ideal for rapid charging stations.
- While AC dominates inside homes and businesses for slower overnight charging, and DC is best for rapid highway charging, both AC and DC chargers can be found in various locations. The power level capabilities are the primary distinguishing factor between AC and DC chargers, not necessarily just the location type. With DC’s ultra-fast charging, and AC’s slower but cheaper and more widespread infrastructure, both technologies have an important role for EV charging.